Services
DDC provides a wide range of qualitative and quantitative research services, as well as strategic consulting, across various sectors: E-commerce – Consumer goods – Finance – Technology, etc.
Market Segmentation and Brand Positioning
These are two important concepts in marketing and business strategy, helping companies better understand their customers and develop appropriate strategies to compete in the market.
Market Segmentation
Concept: Market segmentation is the process of dividing a large market into smaller, more homogeneous groups based on needs, preferences, and consumer behavior. The goal is to understand each customer group better and develop targeted marketing strategies for each segment.
Market Segmentation Criteria:
- Geographic Segmentation: It is based on the geographic location of customers such as country, region, city, or area.
- Demographic Segmentation: It is based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, occupation, and marital status.
- Psychographic Segmentation: It is based on lifestyle, values, interests, and attitudes of customers.
- Behavioral Segmentation: It is based on customer behavior related to the product such as usage level, loyalty, and response to promotional programs.
- Create products and services that meet the specific needs of each customer group.
- Enhance the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by focusing on customer groups with similar needs.
Brand Positioning
Concept: Brand positioning is the process of creating and maintaining a specific image of the brand in the minds of target customers. The goal is to make the brand stand out and differentiate itself from competitors in the same market.
Steps in Brand Positioning:
- Identify Target Market: Understand the market segments that the brand aims to target.
- Determine Brand Strengths and Weaknesses: Analyze what makes the brand unique and the benefits it provides.
- Analyze Competitors: Understand competitors and how they position their brands.
- Develop Positioning Message: Create a clear and consistent message about the brand’s strengths and benefits.
- Communicate Positioning Message: Use marketing and communication strategies to convey the positioning message to target customers.
- Create a clear and differentiated brand image in the minds of customers.
- Build brand recognition and customer loyalty by providing unique value and meeting the needs of the target market.
The Relationship Between Market Segmentation and Brand Positioning:
- Market Segmentation helps identify specific target customer groups based on their needs and unique characteristics.
- Brand Positioning is then developed to meet the needs and expectations of these market segments, ensuring that the brand stands out and is clearly recognized within each segment.
Exploring Consumer Attitudes and Behaviors
This is the process of studying to understand consumer perspectives, emotions, and behaviors towards products, services, or brands, thereby helping companies or organizations adjust marketing strategies, develop products, and improve customer experience.

User Attitudes
Concept: User attitude is the collection of views, feelings, and evaluations that consumers have about a product, service, or brand. Attitudes can include preferences, dissatisfaction, or neutrality towards a product or brand.
Factors in User Attitude:
- Like or Dislike: Positive or negative feelings towards a product or brand.
- Quality Assessment: Perception of the quality and value of the product or service.
- Trust: The level of trust in the brand or company.
- Prejudices and Acceptance: Prior opinions and the level of willingness to accept new products or changes.
- Surveys: Using structured questions to collect information about user feelings and evaluations.
- Interviews: Direct interaction to gain deeper understanding of user perspectives and feelings.
- Focus Groups: Group discussions with users to gather opinions and impressions about a product or service.
User Behavior
Concept: User behavior refers to the actions and habits that consumers exhibit related to the use of products, services, or brands. This includes how consumers search for, select, purchase, and use products.
Factors in User Behavior:
- Shopping Behavior: The steps and decisions involved in the purchasing process, from searching for information to making a purchase decision.
- Product Usage: How consumers use products or services in practice.
- Consumption Habits: The habits and trends in consuming products or services.
- Feedback and Interaction: How consumers provide feedback and interact with the company or product, including complaints, reviews, and suggestions.
- Data Analytics: Using data from transaction systems, websites, and applications to understand shopping behavior and product usage.
- Web Analytics: Tracking and analyzing user behavior on websites and online platforms.
- Field Research: Observing and recording user behavior in real-world settings to understand how they interact with products or services.
Relationship Between Attitude and User Behavior
- Attitude often influences behavior. For example, if consumers have a positive attitude toward a product, they may be more likely to purchase it more often or recommend it to others.
- Behavior can provide additional insights into attitude. For example, analyzing consumer shopping behavior can help understand their preferences or dissatisfaction with a product.
Retail Measurement
This is the process of collecting, analyzing, and evaluating data related to retail activities to better understand performance, customer behaviors, and market trends.

Aspects of Retail Measurement
- Sales and Average Sales:
- Sales: The total amount of money earned from sales over a specific period.
- Average Sales: The average revenue per transaction or per customer, helping to assess the effectiveness of sales and pricing strategies.
- Transaction Frequency and Volume:
- Transaction Frequency: The number of transactions conducted over a specific period.
- Transaction Volume: The total quantity of goods sold over a specific period.
- Customer Satisfaction:
- Satisfaction Surveys: Assessing the level of customer satisfaction with products, services, and shopping experience.
- NPS (Net Promoter Score): Measuring the likelihood that customers will recommend the store or product to others.
- Customer Retention Rate:
- Customer Retention Rate: Measuring the percentage of customers who return to make repeat purchases over a specific period.
- Product Performance:
- Product Revenue: Assessing revenue generated by each product or product group to determine which products are bestsellers or not.
- Inventory Turnover: Monitoring inventory levels to manage supply and minimize stockouts or excessive inventory.
- Marketing Effectiveness:
- Advertising Campaign Results: Evaluating the effectiveness of advertising and promotional campaigns by analyzing sales data during promotion periods.
- Marketing Cost per Transaction: Calculating the marketing cost needed to achieve each sales transaction.
- Customer Shopping Behavior:
- Behavior Analysis: Tracking how customers interact with the store or website, including time spent, products considered, and purchase decisions.
- Store Performance Metrics:
- Revenue per Square Foot: Assessing revenue based on store area to compare performance between stores.
- Revenue per Employee: Calculating the revenue generated by each sales employee to evaluate labor efficiency.
Retail Measurement Tools
- Point of Sale (POS) Systems: Provide detailed data on sales transactions, revenue, and product performance.
- Data Analytics: Utilize data analytics tools to process and understand information from retail data sources.
- Surveys and Customer Feedback: Collect customer opinions to assess satisfaction and improve services.
Importance of Retail Measurement
- Optimize Performance: Helps retail managers understand store performance and sales strategies.
- Improve Customer Experience: Provides information to enhance service quality and customer satisfaction.
- Make Informed Decisions: Supports strategic decisions based on specific data about customer behavior and needs.
Brand Health Evaluation
This is the process of analyzing and measuring key indicators to understand the current state of a brand, identify opportunities and challenges, and develop strategies to improve and maintain the brand's position.
Key Components in Brand Health Assessment
- Brand Awareness:
- Brand Recognition: Measures how well customers can recognize or recall the brand. This can be assessed through brand recognition surveys among target customers.
- Visual Recognition: Assesses the ability to recognize the brand through visual elements such as logos, colors, and packaging design.
- Brand Reputation:
- Reputation Assessment: Measures the trust and credibility of the brand in the eyes of customers and the public.
- Customer Feedback: Analyzes customer feedback and reviews to understand satisfaction levels and potential issues.
- Brand Preference and Satisfaction:
- Preference: Evaluates customer preference and favorability towards the brand compared to competitors.
- Satisfaction: Measures the level of satisfaction customers have with the brand’s products or services.
- Brand Loyalty:
- Customer Retention Rate: Measures the rate at which customers return and continue to make purchases from the brand.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures the likelihood of customers recommending the brand to others.
- Brand Performance:
- Revenue and Market Share: Assesses brand success based on revenue, market share, and other financial indicators.
- Marketing Effectiveness: Evaluates the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and advertisements in generating revenue and brand recognition.
- Brand Positioning:
- Mindshare: Assesses the brand’s position relative to competitors in the minds of customers.
- Brand Messaging: Evaluates the clarity and effectiveness of the brand’s messaging in conveying its values and differentiators.
- Innovation and Development:
- Product Innovation: Assesses the brand’s ability to innovate and develop new products or services.
Tools and Methods for Brand Health Assessment
- Surveys and Interviews: Collects opinions and feedback from customers to understand brand recognition, reputation, and satisfaction.
- Data Analysis: Uses sales data, web analytics, and analytical tools to assess brand performance.
- Market Research: Conducts market research to compare the brand with competitors and understand market trends.
- Online Sentiment Analysis: Analyzes feedback and reviews on social media and online platforms to assess brand reputation and image.
Importance of Brand Health Assessment
- Improving Marketing Strategies: Provides essential information to adjust marketing strategies and develop more effective advertising campaigns.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Helps identify issues in customer experience and develop solutions to improve satisfaction.
- Maintaining and Strengthening Brand Position: Helps maintain and enhance the brand’s market position by understanding factors affecting brand health.
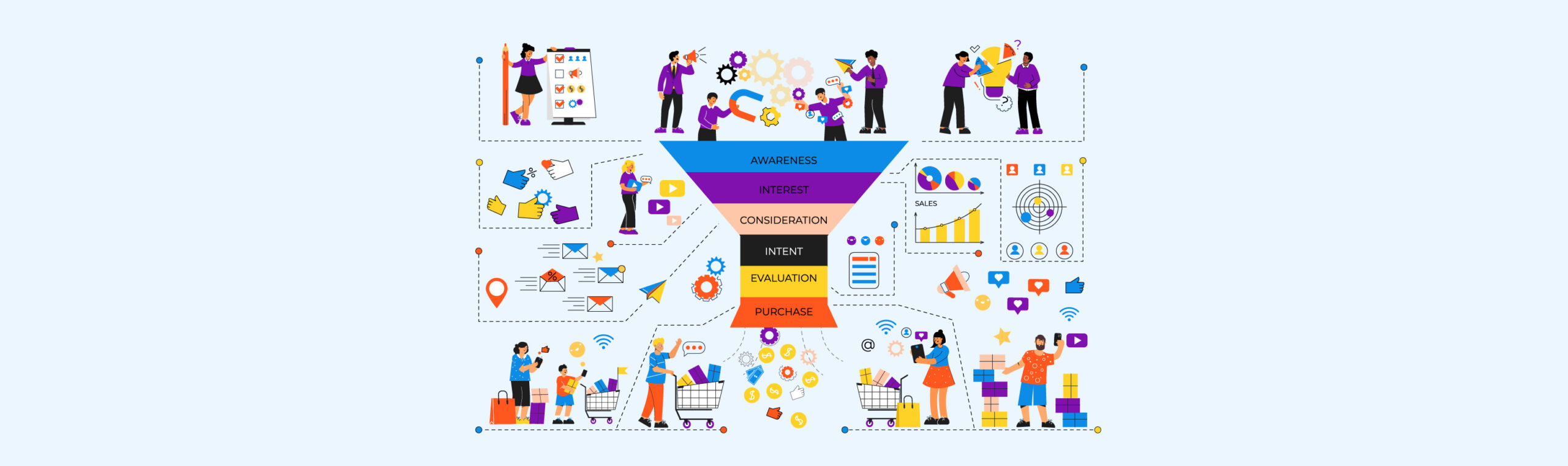
Identifying Customer Purchase Journey
This is the process of analyzing and describing the steps customers go through from becoming aware of a product or service to completing a transaction and even post-purchase, in order to optimize touchpoints and enhance customer satisfaction.

Stages in the Purchase Journey
- Awareness:
- Customers recognize a need or problem and start searching for information to address it.
- Touchpoints: Advertising, social media, traditional media, recommendations from friends or family, online searches.
- Consideration:
- Customers begin researching available options and comparing different products or services.
- Touchpoints: Company websites, product reviews, product comparisons, sales staff consultations, tutorial videos.
- Decision:
- Customers make a decision to purchase and select a specific product or service.
- Touchpoints: Checkout process on the website, customer support, return policies, promotions, and discounts.
- Purchase:
- Customers complete the transaction and finalize their purchase.
- Touchpoints: Payment page, delivery, customer service, invoices, and order confirmations.
- Post-Purchase Experience:
- Customers use the product or service and evaluate their overall experience.
- Touchpoints: After-sales support, customer service, product feedback and reviews, loyalty programs.
- Loyalty and Advocacy:
- Customers become brand advocates and may recommend the product or service to others.
- Touchpoints: Loyalty programs, satisfaction surveys, promotions for loyal customers.
Methods for Determining the Purchase Journey
- Interviews and Surveys:
- Gather direct feedback from customers about their experiences at each stage of the purchase journey.
- Data Analysis:
- Use data from web analytics tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and transaction data to understand customer behavior.
- Market Research:
- Conduct market research to understand consumer trends and behaviors, thereby building a model of the purchase journey.
- Behavior Tracking:
- Track customer behavior across online and offline platforms to identify touchpoints and actions.
- Focus Groups:
- Organize discussion groups with customers to gather insights about their experiences and purchase journeys.
Benefits of Determining the Purchase Journey
- Improving Customer Experience: Helps identify pain points and opportunities to enhance customer experience at each stage.
- Optimizing Touchpoints: Aids in optimizing customer touchpoints to increase the effectiveness of marketing and sales strategies.
- Enhancing Marketing Effectiveness: Provides insights for developing marketing campaigns targeted at specific stages of the purchase journey.
- Building Loyalty: Improves post-purchase experience and fosters customer loyalty through support programs and services.
Evaluating Ideas / Packaging / Products / Pricing / Advertising
This is the process of analyzing and evaluating packaging design / ideas / products to determine effectiveness, attractiveness, and ability to meet market needs.

Packaging Evaluation
Concept: Packaging evaluation is the process of inspecting and analyzing the elements of a product’s packaging, including design, materials, functionality, and labeling, to determine its effectiveness and appeal to customers.
Elements to Evaluate:
- Design and Visual Appeal:
- Aesthetics: Does the packaging have an attractive design that aligns with the brand image?
- Visibility: Is the packaging noticeable and able to attract customer attention in a retail environment?
- Material and Durability:
- Material: Is the packaging made from suitable and high-quality materials?
- Durability: Does the packaging effectively protect the product during transportation and storage?
- Functionality and Convenience:
- Ease of Use: Is the packaging easy to open, close, and use?
- Features: Does the packaging have special features such as leak-proofing or good preservation?
- Information and Labeling:
- Product Information: Does the packaging provide complete information about the product, including usage instructions and necessary details?
- Readability: Is the information on the packaging easy to read and understand?
- Brand Recognition:
- Brand Visibility: Does the packaging enhance brand recognition?
- Consistency: Is the packaging design consistent with other brand elements?
- Customer Surveys: Collect customer feedback on packaging to understand satisfaction and identify potential issues.
- Focus Groups: Conduct group discussions with customers to receive feedback on packaging design and functionality.
- Market Testing: Introduce the packaging in a test market to evaluate customer reactions and sales effectiveness.
Idea Evaluation
Concept: Idea evaluation is the process of analyzing and assessing new product or strategy ideas to determine their feasibility, market potential, and alignment with customer needs.
Elements to Evaluate:
- Feasibility:
- Technical: Is the idea technically and manufacturably feasible?
- Cost: Are the development and production costs reasonable?
- Market Potential:
- Demand: Does the idea address market needs and desires?
- Competition: Can the idea compete with existing products in the market?
- Innovation:
- Uniqueness: Does the idea offer new value or improvements over current products?
- Creativity: Is the idea sufficiently creative and appealing?
- Customer Feedback:
- Surveys: Use surveys to gather customer opinions on the idea.
- Focus Groups: Conduct focus groups to receive detailed feedback on the idea.
- Consistency:
- Brand Strategy: Does the idea align with the current brand strategy and image?
- Objectives: Does the idea support business and marketing objectives?
- Idea Surveys: Gather feedback from customers, partners, and stakeholders about the idea.
- SWOT Analysis: Assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the idea.
- Market Research: Analyze the market to understand demand and trends related to the idea.
Importance of Packaging and Idea Evaluation
- Enhance Sales Effectiveness: Ensures that packaging and product ideas meet customer needs and support sales strategies.
- Improve Customer Experience: Creates attractive and user-friendly packaging and product ideas, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Ensure Competitiveness: Helps products stand out in the market and compete effectively with other products.
Application Evaluation (UI/UX)
This is the process of analyzing and evaluating the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design of an application to ensure that it is effective, user-friendly, and meets user needs.

Key Components in UI/UX Evaluation
- User Interface (UI) Evaluation:
- Visual Design: Assess the layout of elements on the interface, including color, typography, images, and icons. The design should be attractive, consistent with the brand, and visually accessible.
- Consistency: Ensure that interface elements are used consistently across the application to avoid user confusion.
- Usability: Evaluate the ease of use of interface components, such as buttons, menus, and forms. These components should be easily recognizable and usable.
- Responsive Design: Check how the application performs across different devices and screen sizes to ensure the interface remains effective.
- User Experience (UX) Evaluation:
- Navigation: Assess the logic and ease of navigation within the application, ensuring users can find functions and information easily.
- Overall User Experience: Evaluate the user’s overall experience with the application, including perceptions of speed, smoothness, and responsiveness.
- User Interaction: Assess how users interact with the application, including feedback from their actions and how the application handles these interactions.
- Efficiency: Evaluate the time and effort required to complete tasks within the application, ensuring users do not face difficulties or excessive delays.
Methods of UI/UX Evaluation:
- User Surveys:
- Collect feedback from users about the interface and their experience to understand satisfaction levels and areas for improvement.
- User Interviews:
- Conduct in-depth interviews with users to gather detailed opinions about their experience with the application.
- Focus Groups:
- Organize discussion groups with users to receive feedback on the design and user experience of the application.
- User Testing:
- Monitor users performing specific tasks in the application to assess usability and identify issues.
- Data Analytics:
- Use data analytics tools to track user behavior within the application, such as exit rates, usage time, and key touchpoints.
- Compatibility Testing:
- Assess how the application performs across different platforms and devices, including operating systems and screen sizes.
Benefits of UI/UX Evaluation:
- Enhance User Experience: Ensures the application is easy to use, engaging, and meets user needs, thereby improving satisfaction and user retention.
- Increase Efficiency: Helps optimize the interface and experience, minimizing errors and user task completion times.
- Reduce Bounce Rates: Improves design and experience to lower the rate of users abandoning the application or discontinuing use.
- Enhance Competitiveness: Introduces innovative improvements to stand out among competing applications in the market.
Observing Consumer Behavior: Online & Offline
This is a market research method that helps collect data on how consumers interact with products, services, and brands in different environments.

Online Consumer Behavior Observation
Concept: Observing online consumer behavior focuses on tracking and analyzing consumer actions when interacting with online platforms such as websites, social media, mobile apps, and e-commerce platforms.
Methods:
- Web Analytics:
- Website Data: Track metrics such as traffic, time on page, bounce rate, and user journey.
- Tools: Google Analytics, Hotjar, and other web analytics tools.
- Social Media Monitoring:
- Interaction Analysis: Monitor consumer activities on social media, including likes, comments, and shares.
- Tools: Hootsuite, Sprout Social, and other social media analytics tools.
- Transaction Data Analysis:
- Online Shopping Data: Track shopping transactions, selected products, and purchase-related behaviors.
- User Behavior Tracking:
- Behavior Recording: Use tools to record user actions on websites or apps, such as clicks, page scrolling, and interactions with interface elements.
- Online Surveys and Interviews:
- User Surveys: Collect feedback from consumers about their online experiences through surveys and interviews.
- Accurate and Detailed Data: Provides insights into specific consumer behaviors and is easy to track in real-time.
- Optimize User Experience: Helps improve website design, app functionality, and online marketing strategies.
Offline Consumer Behavior Observation
Concept: Observing offline consumer behavior focuses on tracking and analyzing consumer actions in physical environments such as stores, supermarkets, trade shows, and other offline events.
Methods:
- In-Store Observation:
- Shopping Behavior: Track how consumers move through the store, the products they view and select, and their interactions with sales staff.
- Tools: Security cameras, direct notes, and store behavior analysis software.
- Store Experiments:
- Display Changes: Conduct experiments on product displays, lighting, and other factors to assess their impact on shopping behavior.
- On-Site Surveys:
- Customer Surveys: Collect opinions and feedback from customers on-site at stores or events through quick surveys or interviews.
- Event Tracking:
- Events and Trade Shows: Observe consumer behavior at special events, including how they interact with booths and activities at the event.
- Sales Data Analysis:
- Sales Data: Track data on the number and type of products sold in stores to better understand shopping behavior.
- Understanding Offline Behavior: Provides insights into how consumers interact with products and brands in physical environments.
- Optimize Store Layout: Helps improve product arrangement and store design to enhance sales effectiveness.
Importance of Consumer Behavior Observation
- Improve Customer Experience: Helps understand consumer needs and desires to enhance customer experience.
- Optimize Marketing Strategies: Provides crucial data to develop more effective marketing strategies.
- Increase Sales Efficiency: Helps adjust in-store and online factors to optimize revenue and profitability.
Assessing Customer Satisfaction
This is the process of measuring and analyzing customer satisfaction with a product, service, or overall experience they receive from a business, in order to improve and optimize their experience.

Key Factors in Customer Satisfaction Evaluation
- Product/Service Quality:
- Fit: Does the product or service meet the customer’s needs and expectations?
- Performance: Does the product or service perform as expected?
- Customer Service:
- Support: Are staff providing timely and effective support?
- Attitude: Is the staff’s attitude friendly and professional?
- Shopping Experience:
- Ease: Is the shopping process easy and convenient?
- Timing: Are order processing and delivery times reasonable?
- Value for Money:
- Pricing: Is the price of the product or service reasonable compared to the value received?
- Promotions: Are promotional programs and offers attractive and fair?
- Consistency:
-
- Consistent Experience: Is the customer experience consistent across different channels and times?
-
Methods for Evaluating Customer Satisfaction
- Customer Surveys:
- Quantitative Questions: Use quantifiable questions to measure satisfaction levels, such as a scale from 1 to 10.
- Qualitative Questions: Gather detailed feedback about the customer’s experience.
- Customer Interviews:
- Direct Interviews: Interact directly with customers to collect in-depth and detailed information about their satisfaction.
- Focus Groups:
- Group Discussions: Organize group discussions with customers to understand their feelings and opinions better.
- Transaction Data Analysis:
- Shopping Data: Analyze data from transactions to understand shopping behavior and customer trends.
- Review Monitoring:
- Online Reviews: Monitor and analyze customer reviews and feedback on online platforms.
Benefits of Customer Satisfaction Evaluation
- Improvement of Services and Products: Identify strengths and weaknesses in services or products for necessary improvements.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: Understanding and meeting customer needs helps build loyalty and improve customer retention.
- Optimized Marketing Strategies: Satisfaction survey data helps develop more effective marketing strategies.
- Early Issue Detection: Identify and address issues before they become major concerns.
Evaluating customer satisfaction is a critical tool that helps businesses understand customer needs and expectations better, leading to improvements in product and service quality.
DATA APPLICATION JOINT STOCK COMPANY
We ensure accurate and timely market research information.
Quick Access
Policies and Payments
Information
- Mplaza Building, 39 Le Duan, Ben Nghe Ward, District 1, Ho Chi Minh City
- 0986 287 226 (Ms. Hà)
- hello@ddc-global.com
